还在编写 DLL?
让我们来解放你!
简介
MQL5 语言的功能性总是有不足以完成任务的时刻。在这种情况下,MQL5 程序员不得不使用其他工具。例如,可以使用数据库、使用通信套接字或利用操作系统的功能。MQL5 程序员还需要处理各种 API 以扩展其使用的 MQL5 程序的可能性。但基于几个原因,程序员无法直接从 MQL5 访问所需的功能,因为他们不知道:
- 如何将一个复杂的数据类型(例如结构)传递至 API 函数;
- 如何使用 API 函数返回的指针。
因此,程序员被迫使用其他的编程语言,并创建中间 DLL 以使用所需的功能。尽管 MQL5 可提供各种数据类型并将它们传递至 API,但遗憾的是,MQL5 无法解决从收到的指针提取数据的相关问题。
在本文中,我们将循规蹈矩,说明传递和接收复杂数据类型以及使用返回的指针的简单机制。
目录
- 获取指针
- 复制内存区域
- 使用 MQL5 转换结构
- 为套接字传递结构的示例
- 内存映射文件示例
- MySQL 示例
1. 内存就是一切
正如您可能知道的,任何变量(包括复杂数据类型变量)都有其特定的地址,变量就存储在内存的该位置。这个地址是一个四字节的整数值(int 类型),等于这个变量第一个字节的地址。
如果一切定义得当,就可以使用此内存区域。C 语言函数库 (msvcrt.dll) 包含 memcpy 函数。其目的是缺失元素,这些缺失元素将 MQL5 和各种 API 库结合起来,并为程序员提供了极大的发挥空间。
让我们转向前辈留下的相关知识
Memcpy 函数从一个缓冲区复制指定数量的字节至另一个缓冲区,并将指针返回接收缓冲区。
void *memcpy(void *dst, const void *src, int cnt); dst - pointer to the receiver buffer src - pointer to the source buffer cnt - number of bytes for copying
换言之,一个大小为 cnt 字节起始于 src 地址的内存区域被复制到起始于 dst 地址的内存区域。
位于 src 地址的数据可以是多种类型。这可能是 1 字节的 char 变量,8 字节的 double 数值,数组,或是任意内存大小的任意结构。这意味着,只要知道地址和大小,您可以随意地将数据从一个区域传输到另一个区域。
工作原理
图 1 显示了部分数据类型的相对大小。

需要 Memcpy 函数以将数据从一个内存区域复制到另一个内存区域。
图 2 显示 4 字节复制。
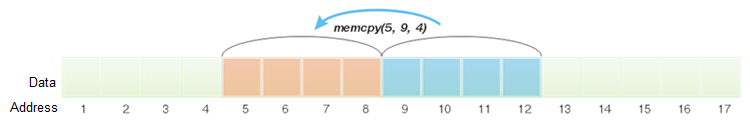
在 MQL5 中,该过程如下所示。
Example 1. Using memcpy #import "msvcrt.dll" int memcpy(int &dst, int &src, int cnt); #import //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { int dst, src=4, cnt=sizeof(int); int adr=memcpy(dst, src, cnt); Print("dst value="+string(dst)+" Address dst="+string(adr)); }
需要注意的是,多种数据类型(具有相同的 cnt 大小)可用于 dst 和 src 指向的内存区域。例如,src 指针可指向 double 变量(cnt=8 字节),dst 可指向具有同样大小 char[8] 或 int[2] 的数组。
程序员当时的想法对于内存而言无关紧要。无论是一个数组 char[8] 或只是一个 long 变量还是结构 { int a1; int a2; }都无关紧要。
可以将内存数据视为各种类型的数据。例如,可以传递 5 字节的数组至 {int i; char c;} 结构,反之亦然。这种关系提供了直接使用 API 函数的机会。
我们按一定的顺序来查看一下 memcpy 应用程序的版本。
获取指针
在例 1 中我们发现,memcpy 函数返回 dst 变量的地址。
这一属性可用于获取任意变量(包含其他复杂类型的数组)的地址。为此,我们只需要指定同一变量作为源参数和接收参数。在 cnt 中,由于实际复制没有必要,可以传递 0。
例如,我们可以获得 double 变量和 short 数组的地址:
Example 2. Getting pointers to the variable #import "msvcrt.dll" int memcpy(short &dst[], short &src[], int cnt); int memcpy(double &dst, double &src, int cnt); #import //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { short src[5]; //--- getting src array address (i.е., the address of the first element) int adr=memcpy(src, src, 0); double var; //--- getting var variable address adr=memcpy(var, var, 0); }
然后接收到的地址可以被传递至所需 API 函数或作为结构参数,也可以作为同一 memcpy 函数的参数。
复制数组
如您所知,数组是一些专用的内存块。专用内存的大小取决于元素的类型及其数量。例如,如果数组元素的类型为 short 且元素数量为 10,这样一个数组在内存中占据 20 字节(short 大小为 2 字节)。
但是,这 20 字节也可以由 20 char 或 5 int 组成。无论如何,它们在内存中占据相同的 20 字节。
要复制数组,必须执行下述操作:
- 为 dst 内存分配要求的元素数量(不少于结果 cnt 字节);
- 在 cnt 中指定须从 src 复制的字节数。
Example 3. Copying the arrays #import "msvcrt.dll" int memcpy(double &dst[], double &src[], int cnt); #import //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { double src[5]; //--- calculating the number of bytes!!! int cnt=sizeof(double)*ArraySize(src); double dst[]; ArrayResize(dst, 5); //--- the array has been copied from src to dst memcpy(dst, src, cnt); }
2. 将结构传递至 API 函数
假设您需要传递填充结构指针至 API。MQL5 语言针对结构的传递设置了限制。在本文的一开始,我已声明内存可以用不同的形式表示。这意味着可以将需要的结构复制到 MQL5 支持的数据类型。一般而言,数组是较为适合结构的类型。因此,我们需要从结构获得数组,然后将数组传递至 API 函数。
使用结构复制内存的选项在文档部分中说明。我们无法使用 memcpy 函数,因为它无法将结构作为参数传递,在这里复制结构是唯一的方法。
图 3 显示了包含 5 个不同类型变量的结构的表示,及其 char 数组形式的等效表示。
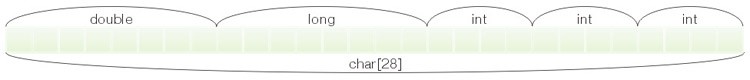
Example 4. Copying the structures by means of MQL5 struct str1 { double d; // 8 bytes long l; // 8 bytes int i[3]; // 3*4=12 bytes }; struct str2 { uchar c[8+8+12]; // str1 structure size }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { str1 src; src.d=-1; src.l=20; //--- filling the structure parameters ArrayInitialize(src.i, 0); str2 dst; //--- turning the structure into the byte array dst=src; }
通过这种简单的方式,我们将结构复制到字节数组中。
我们考虑套接字 创建函数,以使这个示例更为实用。
int connect(SOCKET s, const struct sockaddr *name, int namelen);
在这个函数中,第二个参数是有问题的,因为它接收结构的指针。但我们已经知道了要用它来做什么。那么,我们开始吧。
1. 我们通过 MQL5 中允许的方法编写用于导入的连接函数:
int connect(int s, uchar &name[], int namelen);
2. 在文档中观察所需结构:
struct sockaddr_in { short sin_family; u_short sin_port; in_addr sin_addr; // additional 8 byte structure char sin_zero[8]; };
3. 使用相同大小的数组创建结构:
struct ref_sockaddr_in { uchar c[2+2+8+8]; };
4. 填充所需的 sockaddr_in 结构后,将其传递至字节数组并作为 connect 参数提交。
下面是根据这些步骤编写的代码段。
Example 5. Referring of the client socket to the server #import "Ws2_32.dll" ushort htons(ushort hostshort); ulong inet_addr(char &cp[]); int connect(int s, char &name[], int namelen); #import //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- connecting the host after the socket initialization char ch[]; StringToCharArray("127.0.0.1", ch); //--- preparing the structure sockaddr_in addrin; addrin.sin_family=AF_INET; addrin.sin_addr=inet_addr(ch); addrin.sin_port=htons(1000); //--- copying the structure to the array ref_sockaddr_in ref=addrin; //--- connecting the host res=connect(asock, ref.c, sizeof(addrin)); //--- further work with the socket }
看到了吧,您完全不需要编写自己的 DLL。结构被直接传递到 API。
3. 使用 API 函数指针
大多数情况下,API 函数返回指针至:结构和数组。MQL5 不适于提取数据,在此我们可以使用 memcpy 函数。
从内存映射文件 (MMF) 使用内存数组的示例
使用 MMF 时函数使用,以返回指针至专用内存数组。
int MapViewOfFile(int hFile, int DesiredAccess, int OffsetHigh, int OffsetLow, int NumOfBytesToMap);
从此数组读取数据通过 memcpy 函数简单复制所需的字节数实现。
将数据写入数组同样通过使用 memcpy 函数实现。
Example 6. Recording and reading data from MMF memory #import "kernel32.dll" int OpenFileMappingW(int dwDesiredAccess, int bInheritHandle, string lpName); int MapViewOfFile(int hFileMappingObject, int dwDesiredAccess, int dwFileOffsetHigh, int dwFileOffsetLow, int dwNumberOfBytesToMap); int UnmapViewOfFile(int lpBaseAddress); int CloseHandle(int hObject); #import "msvcrt.dll" int memcpy(uchar &Destination[], int Source, int Length); int memcpy(int Destination, int &Source, int Length); int memcpy(int Destination, uchar &Source[], int Length); #import #define FILE_MAP_ALL_ACCESS 0x000F001F //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- opening the memory object int hmem=OpenFileMappingW(FILE_MAP_ALL_ACCESS, 0, "Local//file"); //--- getting pointer to the memory int view=MapViewOfFile(hmem, FILE_MAP_ALL_ACCESS, 0, 0, 0); //--- reading the first 10 bytes from the memory uchar src[10]; memcpy(src, view, 10); int num=10; //--- recording the 4 byte int number to the memory beginning memcpy(view, num, 4); //--- unmapping the view UnmapViewOfFile(view); //--- closing the object CloseHandle(hmem); }
如您所见,将指针用于内存数组并不是很难。更重要的是,您无需为此创建额外的 DLL。
将返回的结构用于 MySQL 的示例
使用 MySQL 时一个亟待解决的问题就是从中获得数据。mysql_fetch_row 函数返回字符串数组。每个字符串是一个字段数组。因此,这个函数返回指针至指针。我们的任务是从返回的指针中提取所有这些数据。
该任务有一点复杂,因为字段可以是包括二进制在内的多种数据类型。这意味着不可能以 string 数组来表示它们。函数 mysql_num_rows、mysql_num_fields、mysql_fetch_lengths 用于获取有关字符串和字段大小的信息。
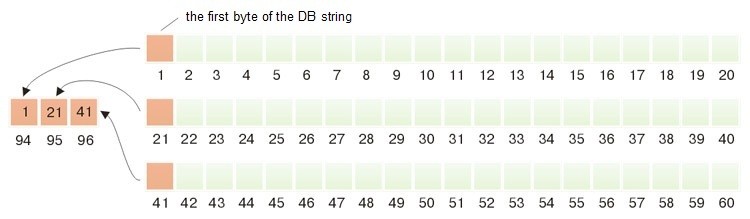
图 4 显示在内存中用于表示结果的结构。
3 个字符串的起始地址位于数组中。而数组的起始地址(本例中为 94)由 mysql_fetch_row 函数返回。
下面是从数据库请求获取数据的代码示例。
Example 7. Getting data from MySQL #import "libmysql.dll" int mysql_real_query(int mysql, uchar &query[], int length); int mysql_store_result(int mysql); int mysql_field_count(int mysql); uint mysql_num_rows(int result); int mysql_num_fields(int result); int mysql_fetch_lengths(int result); int mysql_fetch_row(int result); #import //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- ... preliminarily initialized mysql data base //--- request for getting all the strings from the table string query="SELECT * FROM table"; uchar aquery[]; StringToCharArray(query, aquery); //--- sending the request err=mysql_real_query(mysql, aquery, StringLen(query)); int result=mysql_store_result(mysql); //--- in case it contains the strings if (result>0) { ulong num_rows=mysql_num_rows(result); int num_fields=mysql_num_fields(result); //--- getting the first string pointer int r=0, row_ptr=mysql_fetch_row(result); while(row_ptr>0) { //--- getting the pointer to the current string columns lengths int len_ptr=mysql_fetch_lengths(result); int lens[]; ArrayResize(lens, num_fields); //--- getting the sizes of the string fields memcpy(lens, len_ptr, num_fields*sizeof(int)); //--- getting the data fields int field_ptr[]; ArrayResize(field_ptr, num_fields); ArrayInitialize(field_ptr, 0); //--- getting the pointers to the fields memcpy(field_ptr, row_ptr, num_fields*sizeof(int)); for (int f=0; f<num_fields; f++) { ArrayResize(byte, lens[f]); ArrayInitialize(byte, 0); //--- copy the field to the byte array if (field_ptr[f]>0 && lens[f]>0) memcpy(byte, field_ptr[f], lens[f]); } r++; //--- getting the pointer to the pointer to the next string row_ptr=mysql_fetch_row(result); } } }
4. 从 API 函数读取以 NULL 结尾的字符串
一些 API 函数返回指针至字符串但不会向我们指出字符串的长度。在这种情形下,我们处理以零结尾的字符串。零帮助判定字符串的结束。这意味着可以指定字符串的大小。
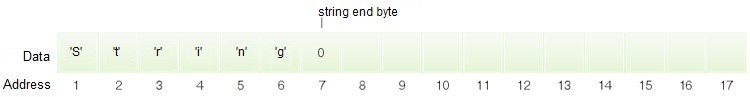
C (msvcrt.dll) 函数库已经有了从适当的指针复制以 NULL 结尾的字符串的内容到其他字符串的函数。字符串的大小由函数定义。最好是使用字节数组作为接收数组,因为 API 通常返回多字节字符串而不是统一码字符串。
strcpy – 复制以 NULL 结尾的字符串
char *strcpy(char *dst, const char *src); dst - the pointer to the destination string src - the pointer to the Null-terminated source string
事实上,它是 memcpy 函数的一个特例。当系统在字符串中找到零时就会停止复制。当使用这种指针时,将始终使用此函数。
例如,在 API 中有多个来自 MySQL 的函数返回指针至字符串。使用 strcpy 获取它们的数据是一项简单的任务。
Example 8. Getting the strings from the pointers #import "libmysql.dll" int mysql_init(int mysql); int mysql_real_connect(int mysql, uchar &host[], uchar &user[], uchar &password[], uchar &DB[], uint port, uchar &socket[], int clientflag); int mysql_get_client_info(); int mysql_get_host_info(int mysql); int mysql_get_server_info(int mysql); int mysql_character_set_name(int mysql); int mysql_stat(int mysql); #import "msvcrt.dll" int strcpy(uchar &dst[], int src); #import //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { uchar byte[]; ArrayResize(byte, 300); int ptr; string st; //--- pointer to the string ptr=mysql_get_client_info(); if (ptr>0) strcpy(byte, ptr); Print("client_info="+CharArrayToString(byte)); //--- initializing the base int mysql=mysql_init(mysql); //--- transferring the strings to the byte arrays uchar ahost[]; StringToCharArray("localhost", ahost); uchar auser[]; StringToCharArray("root", auser); uchar apwd[]; StringToCharArray("", apwd); uchar adb[]; StringToCharArray("some_db", adb); uchar asocket[]; StringToCharArray("", asocket); //--- connecting the base int rez=mysql_real_connect(mysql, ahost, auser, apwd, adb, port, asocket, 0); //--- determining the connection and the base status ptr=mysql_get_host_info(mysql); if (ptr>0) strcpy(byte, ptr); Print("mysql_host_info="+CharArrayToString(byte)); ptr=mysql_get_server_info(mysql); if (ptr>0) strcpy(byte, ptr); Print("mysql_server_info="+CharArrayToString(byte)); ptr=mysql_character_set_name(mysql); if (ptr>0) strcpy(byte, ptr); Print("mysql_character_set_name="+CharArrayToString(byte)); ptr=mysql_stat(mysql); if (ptr>0) strcpy(byte, ptr); Print("mysql_stat="+CharArrayToString(byte)); }
总结
因此,在使用各种 API 函数时,使用内存的三个基本机制的使用(复制结构、通过 memcpy 获取指针及其数据以及获取 strcpy 字符串)几乎涵盖了所有的任务。
警告。使用 memcpy 和 strcpy 可能会不安全,除非已经为接收缓冲区分配了足够的数据。因此,务必留意为接收数据分配的量的大小。
本文译自 MetaQuotes Software Corp. 撰写的俄文原文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/364
MyFxtop迈投(www.myfxtop.com)-靠谱的外汇跟单社区,免费跟随高手做交易!
免责声明:本文系转载自网络,如有侵犯,请联系我们立即删除,另:本文仅代表作者个人观点,与迈投财经无关。其原创性以及文中陈述文字和内容未经本站证实,对本文以及其中全部或者部分内容、文字的真实性、完整性、及时性本站不作任何保证或承诺,请读者仅作参考,并请自行核实相关内容。
著作权归作者所有。
商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。

 MyFxTops邁投財經
MyFxTops邁投財經
