简介
现在,每一位交易者肯定听说过神经网络并知道使用它们有多酷。大多数人相信那些能够使用神经网络的人是某种超人。在本文中,我将尝试向您解释神经网络架构,描述其应用并提供几个实践例子。
神经网络的概念
人工神经网络是人工智能研究的领域之一,以尝试模拟人类的神经系统的学习和适应能力为基础,这会让我们能够建立一个对人类大脑工作的非常粗略的模拟。
说也奇怪,人工神经网络由人工神经元构成。
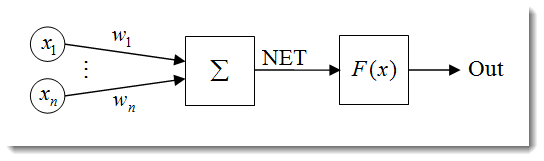
图 1. 人工神经元模型
神经元的结构可表示为以下单元的组合:
- 输入
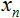 ;
; - 权重
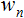 ;
; - 传递函数
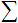 和净输入
和净输入 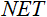 ;
; - 激活函数
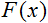 ;
; - 输出
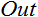 。
。
神经网络有很多特性,学习能力是其中最重要的一个。学习过程实际是改变权重 ![]() 。
。
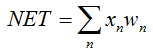
![]() 在这里是神经元的净输入。
在这里是神经元的净输入。
![]()
然后,净输入被激活函数转换为输出;我们将在后面介绍激活函数。简而言之,神经网络可被视为一个接收信号作为输入并输出结果的“黑箱”。
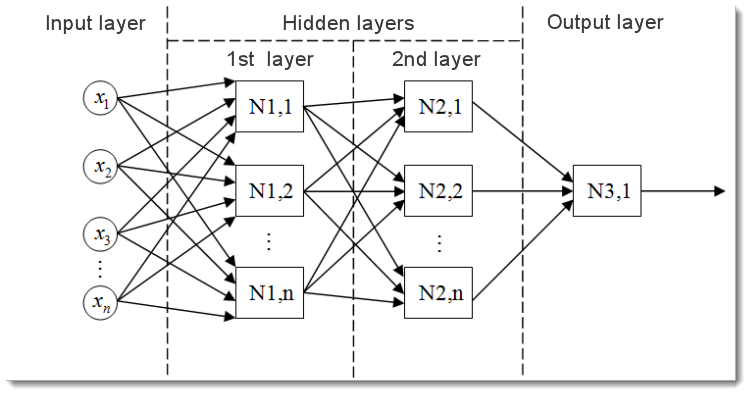
图 2. 多层神经网络模型
这是一个多层神经网络的形式。它包含:
- 输入层,用于将数据分配到网络,并且不执行任何计算。此层的输出将信号传递到下一层(隐藏层或输出层)的输入;
- 输出层,通常包含一个神经元(某些情况下不止一个),生成整个神经网络的输出。此信号是 EA 将来的控制逻辑的基础;
- 隐藏层,是标准神经元层,将信号从输入层传递到输出层。其输入是上一层的输出,而其输出用作下一层的输入。
本例显示了具有两个隐藏层的神经网络。但是某些神经网络可以具有更多的隐藏层。
输入数据正态化
输入数据正态化是对所有数据进行正态化,即减少到 [0,1] 或 [-1,1] 范围内的过程。如果未进行正态化,则输入数据将对神经元有额外的影响,导致错误的决策。换言之,您怎么比较具有不同量级的数值呢?
正态化公式的标准形式如下:
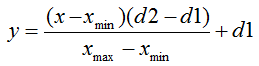
其中:
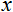 – 要正态的值;
– 要正态的值;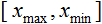 – х 值的范围;
– х 值的范围;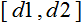 – 要将 x 的值减小到的范围。
– 要将 x 的值减小到的范围。
让我们用一个例子对其进行解释:
假定我们具有 [0,10] 范围内的 n 个输入数据,则 ![]() = 0,
= 0,![]() = 10。我们将数据减小到 [0,1] 范围,则
= 10。我们将数据减小到 [0,1] 范围,则 ![]() = 0,
= 0,![]() = 1。现在,将值插入公式之后,我们可以从 n 个输入数据计算任意 x 的正态值。
= 1。现在,将值插入公式之后,我们可以从 n 个输入数据计算任意 x 的正态值。
以 MQL5 实施时,看起来如下所示:
double d1=0.0; double d2=1.0; double x_min=iMA_buf[ArrayMinimum(iMA_buf)]; double x_max=iMA_buf[ArrayMaximum(iMA_buf)]; for(int i=0;i<ArraySize(iMA_buf);i++) { inputs[i]=(((iMA_buf[i]-x_min)*(d2-d1))/(x_max-x_min))+d1; }
我们首先指定输出值的上限和下限,然后得到指标最大值和最小值(不考虑来自指标的复制数据,但是举例而言,可以有 10 个最后的值)。最后,我们对每一个输入元素(不同柱上的指标值)进行正态化,并将结果存储在一个数组中,供将来使用。
激活函数
激活函数是一种计算神经元输出的函数。它收到的输入表示所有的输入及其对应权重之积的和(以下简称为“加权和”):
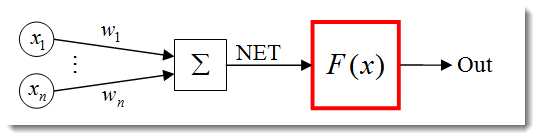
图 3. 突出显示了激活函数的人工神经元模型
激活函数公式的标准形式如下:
![]()
其中:
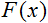 是激活函数;
是激活函数;-
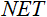 是计算神经元输出的第一阶段获得的加权和;
是计算神经元输出的第一阶段获得的加权和; 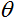 是激活函数的阈值。它仅用于硬阈值函数,在其他函数中等于零。
是激活函数的阈值。它仅用于硬阈值函数,在其他函数中等于零。
激活函数的主要类型如下:
-
单位阶梯函数 或硬阈值函数。
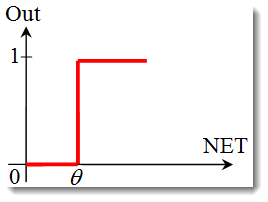
用以下公式描述该函数: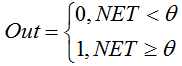
如果加权和小于指定值,则激活函数返回 0。如果加权和大于指定值,则激活函数返回 1。 -
S 形函数。
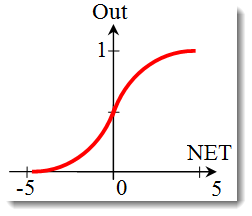
描述 S 函数的公式如下: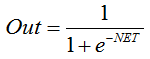
它通常在多层神经网络以及具有连续信号的其它网络中使用。函数光滑度和连续性是非常有用的属性。 -
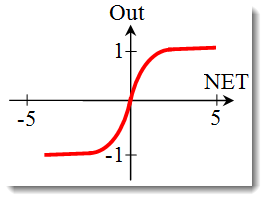
双曲正切函数。
公式: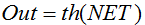 or
or 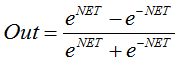
它通常也在具有连续信号的网络中使用。可以返回负值是它的特点。
更改激活函数的形状
在上一节中,我们已经介绍了激活函数的类型。仍然有另一个重要的事项需要考虑 – 函数的斜率(硬阈值函数除外)。让我们更加仔细地观察 S 形函数。
观察函数的图形,可以轻松地看到函数在 [-5,5] 范围内很光滑。假定我们有一个由具有 10 个输入和 1 个输出的单一神经元构成的网络。现在,让我们尝试计算变量 ![]() 的上限值和下限值。每一个输入将从 [-1,1] 范围采用一个正态值(如输入数据正态化)所述)。
的上限值和下限值。每一个输入将从 [-1,1] 范围采用一个正态值(如输入数据正态化)所述)。
我们将使用负的输入值,因为函数在负自变量也是可区分的。也从相同的范围选择权重。使用所有可能的输入和权重组合,我们将获得 [-10,10] 范围内的极值 ![]() ,如下所示:
,如下所示:
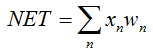
在 MQL5 中,该公式如下所示:
for(int n=0; n<10; n++) { NET+=Xn*Wn; }
现在,我们需要在确定的范围内标绘激活函数。让我们以 S 形函数为例。最简单的方式是使用 Excel。
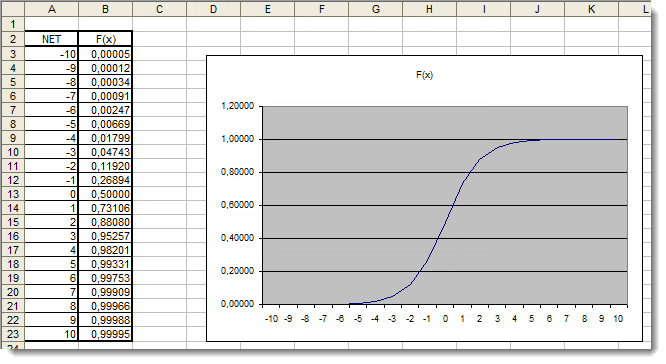
图 4. S 函数在 Excel 中的图形
在这里,我们可以清晰地看到,[-5,5] 范围外的自变量值对结果绝对没有影响。这说明值范围不完整。让我们尝试解决这个问题。我们将向自变量添加一个附加系数 d,这样让我们能够扩展值范围。
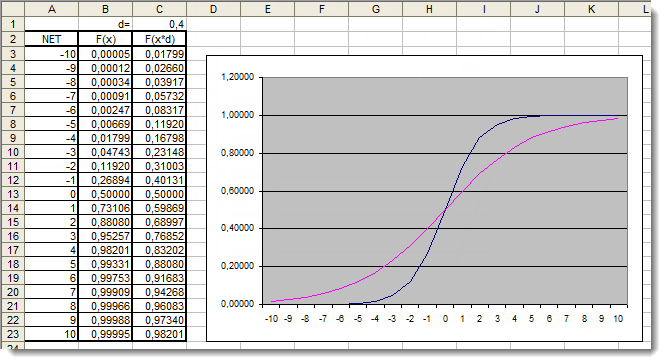
图 5. 应用了附加系数的 S 形函数在 Excel 中的图形
让我们再次观察图形。我们添加了一个附加系数 d=0.4,这改变了函数的形状。对表中的值进行比较,表明现在它们分布更均匀。因此,可以如下表示结果:
for(int n=0; n<10; n++) { NET+=Xn*Wn; } NET*=0.4;
现在,让我们回顾一下双曲正切 激活函数。跳过在回顾上一个函数时介绍的理论,我们立即进行实践应用。在这里,唯一的区别在于输出可在 [-1,1] 的范围内。加权和也可在 [-10,10] 的范围内取值。
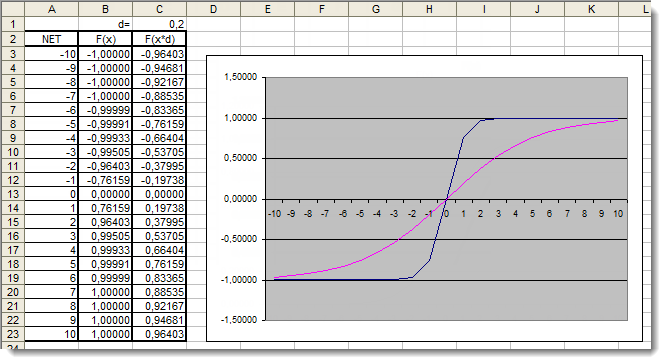
图 6. 应用了附加系数的双曲正切函数在 Excel 中的图形
图形表明,由于使用了附加系数 d=0.2,函数的形状得到改善。因此,可以如下表示结果:
for(int n=0;n<10;n++) { NET+=Xn*Wn; } NET*=0.2;
通过这种方式,您可以改变并改善任何激活函数的形状。
应用
现在,让我们进行实践应用。首先,我们将尝试实施神经元的净输入计算,接着是添加激活函数。让我们回想一下用于计算神经元的净输入的公式:
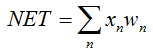
double NET; double x[3]; double w[3]; int OnInit() { x[0]=0.1; // set the input value х1 x[1]=0.8; // set the input value х2 x[2]=0.5; // set the input value х3 w[0]=0.5; // set the weight value w1 w[1]=0.6; // set the weight value w2 w[2]=0.3; // set the weight value w3 for(int n=0;n<3;n++) { NET+=x[n]*w[n]; // add the weighted net input values together } }
让我们观察一下:
- 我们以声明一个用于存储神经元净输入
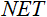 的变量和两个数组:输入
的变量和两个数组:输入 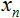 和权重
和权重 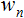 开始;
开始; - 一开始就在所有函数的外部声明这些变量,以让它们具有全局作用范围(从而能够在程序中的任何地方访问);
- 在 OnInit() 初始化函数中(实际上可以是任何其它函数),我们可以填写输入数组和权重数组;
- 接着是求和循环,n<3,因为我们只有三个输入和三个对应的权重;
- 再接着,我们将加权输入值加在一起,并将它们存储在变量
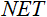 中。
中。
第一项任务已经完成 – 我们得到了和。现在轮到激活函数。以下是用于计算在“激活函数”一节中回顾的激活函数的代码。
单位阶梯函数或硬阈值函数
double Out; if(NET>=x) Out=1; else Out=0;
S 形函数
double Out = 1/(1+exp(-NET));
双曲正切函数
double Out = (exp(NET)-exp(-NET))/(exp(NET)+exp(-NET));
把所有内容串起来
为了让实施更加容易,我们将采用一个由单一神经元构成的网络。称其为网络多少有点牵强,但是重点在于理解原理。总之,一个多层神经网络由相同的神经元构成,其中上一层神经元的输出是下一层的输入。
我们将使用在《初学者快速入门或简明指南》一文中提出并介绍的 EA 的稍有改动的版本。因此,举例而言,我们会将移动平均线趋势指标替换为相对强弱指数振荡指标。可以在内置的帮助中找到有关指标参数及其顺序的信息。
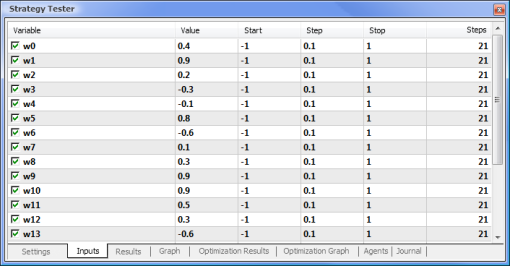
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| neuro-example.mq5 | //| Copyright 2012, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2012, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include <Trade/Trade.mqh> //include the library for execution of trades #include <Trade/PositionInfo.mqh> //include the library for obtaining information on positions //--- weight values input double w0=0.5; input double w1=0.5; input double w2=0.5; input double w3=0.5; input double w4=0.5; input double w5=0.5; input double w6=0.5; input double w7=0.5; input double w8=0.5; input double w9=0.5; int iRSI_handle; // variable for storing the indicator handle double iRSI_buf[]; // dynamic array for storing indicator values double inputs[10]; // array for storing inputs double weight[10]; // array for storing weights double out; // variable for storing the output of the neuron string my_symbol; // variable for storing the symbol ENUM_TIMEFRAMES my_timeframe; // variable for storing the time frame double lot_size; // variable for storing the minimum lot size of the transaction to be performed CTrade m_Trade; // entity for execution of trades CPositionInfo m_Position; // entity for obtaining information on positions //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- save the current chart symbol for further operation of the EA on this very symbol my_symbol=Symbol(); //--- save the current time frame of the chart for further operation of the EA on this very time frame my_timeframe=PERIOD_CURRENT; //--- save the minimum lot of the transaction to be performed lot_size=SymbolInfoDouble(my_symbol,SYMBOL_VOLUME_MIN); //--- apply the indicator and get its handle iRSI_handle=iRSI(my_symbol,my_timeframe,14,PRICE_CLOSE); //--- check the availability of the indicator handle if(iRSI_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) { //--- no handle obtained, print the error message into the log file, complete handling the error Print("Failed to get the indicator handle"); return(-1); } //--- add the indicator to the price chart ChartIndicatorAdd(ChartID(),0,iRSI_handle); //--- set the iRSI_buf array indexing as time series ArraySetAsSeries(iRSI_buf,true); //--- place weights into the array weight[0]=w0; weight[1]=w1; weight[2]=w2; weight[3]=w3; weight[4]=w4; weight[5]=w5; weight[6]=w6; weight[7]=w7; weight[8]=w8; weight[9]=w9; //--- return 0, initialization complete return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { //--- delete the indicator handle and deallocate the memory space it occupies IndicatorRelease(iRSI_handle); //--- free the iRSI_buf dynamic array of data ArrayFree(iRSI_buf); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- variable for storing the results of working with the indicator buffer int err1=0; //--- copy data from the indicator array to the iRSI_buf dynamic array for further work with them err1=CopyBuffer(iRSI_handle,0,1,10,iRSI_buf); //--- in case of errors, print the relevant error message into the log file and exit the function if(err1<0) { Print("Failed to copy data from the indicator buffer"); return; } //--- double d1=0.0; //lower limit of the normalization range double d2=1.0; //upper limit of the normalization range double x_min=iRSI_buf[ArrayMinimum(iRSI_buf)]; //minimum value over the range double x_max=iRSI_buf[ArrayMaximum(iRSI_buf)]; //maximum value over the range //--- In the loop, fill in the array of inputs with the pre-normalized indicator values for(int i=0;i<ArraySize(inputs);i++) { inputs[i]=(((iRSI_buf[i]-x_min)*(d2-d1))/(x_max-x_min))+d1; } //--- store the neuron calculation result in the out variable out=CalculateNeuron(inputs,weight); //--- if the output value of the neuron is less than 0.5 if(out<0.5) { //--- if the position for this symbol already exists if(m_Position.Select(my_symbol)) { //--- and this is a Sell position, then close it if(m_Position.PositionType()==POSITION_TYPE_SELL) m_Trade.PositionClose(my_symbol); //--- or else, if this is a Buy position, then exit if(m_Position.PositionType()==POSITION_TYPE_BUY) return; } //--- if we got here, it means there is no position; then we open it m_Trade.Buy(lot_size,my_symbol); } //--- if the output value of the neuron is equal to or greater than 0.5 if(out>=0.5) { //--- if the position for this symbol already exists if(m_Position.Select(my_symbol)) { //--- and this is a Buy position, then close it if(m_Position.PositionType()==POSITION_TYPE_BUY) m_Trade.PositionClose(my_symbol); //--- or else, if this is a Sell position, then exit if(m_Position.PositionType()==POSITION_TYPE_SELL) return; } //--- if we got here, it means there is no position; then we open it m_Trade.Sell(lot_size,my_symbol); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Neuron calculation function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CalculateNeuron(double &x[],double &w[]) { //--- variable for storing the weighted sum of inputs double NET=0.0; //--- Using a loop we obtain the weighted sum of inputs based on the number of inputs for(int n=0;n<ArraySize(x);n++) { NET+=x[n]*w[n]; } //--- multiply the weighted sum of inputs by the additional coefficient NET*=0.4; //--- send the weighted sum of inputs to the activation function and return its value return(ActivateNeuron(NET)); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Activation function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double ActivateNeuron(double x) { //--- variable for storing the activation function results double Out; //--- sigmoid Out=1/(1+exp(-x)); //--- return the activation function value return(Out); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
我们需要做的第一件事情是训练我们的网络。让我们优化权重。
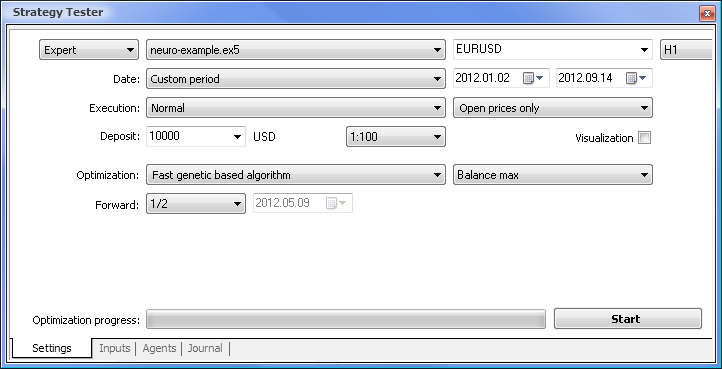
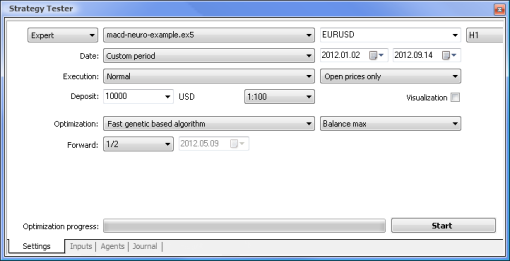
图 7. 设置了所需参数的策略测试程序
我们将使用以下参数运行优化:
- Date(日期) – 具体而言从一年的开头开始。周期越长,曲线拟合出现得就越少,结果也越好。
- Execution(执行) – normal(常规),Opening prices only(仅开盘价)。在 Every tick(每一价格变动)模式中测试没有意义,因为了除了当前值以外,EA 仅采用指标的最后 10 个值。
- Optimization(优化)可设置为使用慢速完整算法运行。然而,基因优化将提供更快的结果,这种优化在评估某个算法时特别有用。如果结果令人满意,也可以使用慢速完整算法以获得更加精确的结果。
- Forward(前进) 1/2 及更多让您能够评估您的 EA 在下一次优化之前要用多才时间才能生成获得的结果。
- Time frame(时间框架)和 Currency pair(货币对)可以依据您的需要设置。
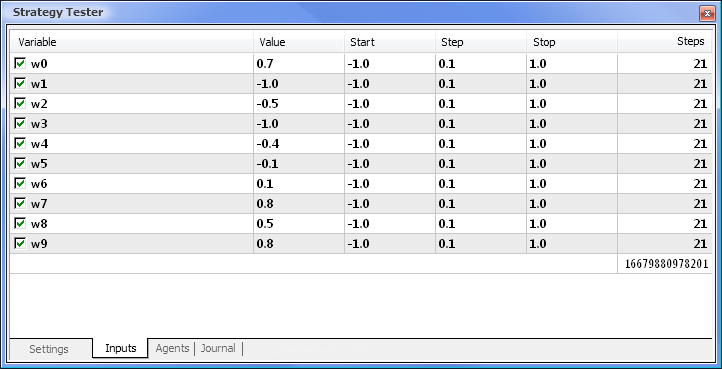
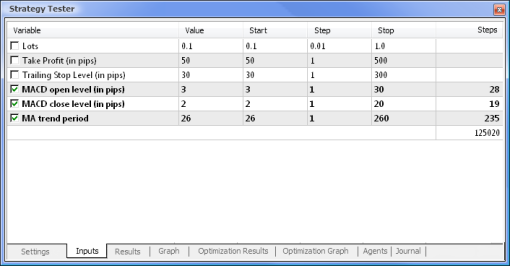
图 8. 设置要优化的参数及它们的相应范围
优化将依据所有权重及它们的范围进行。返回到 Settings(设置)选项卡,然后单击 Start(开始)按钮即可开始优化。
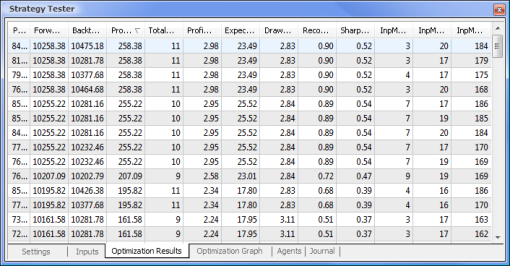
图 9. 在优化之后得到的数据
在优化完成后,我们在 Optimization Results(优化结果)选项卡中选择具有最大盈利值的轮次(要按其中一个参数排序,单击相应的列标题)。然后,您可以评估其他参数并在必要时选择需要的轮次。
双击需要的轮次会开始测试显示在 Results(结果)和 Graph(图形)选项卡中的结果。
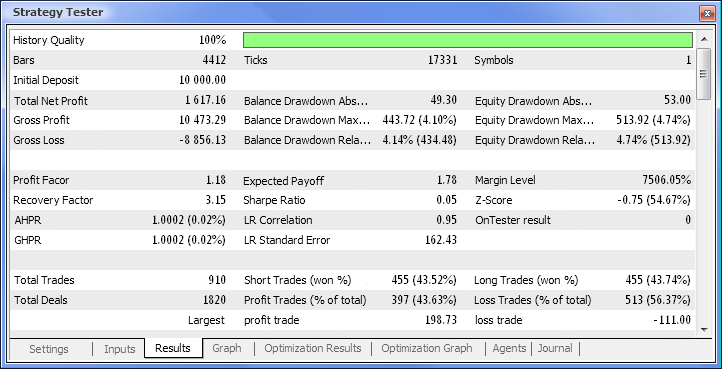
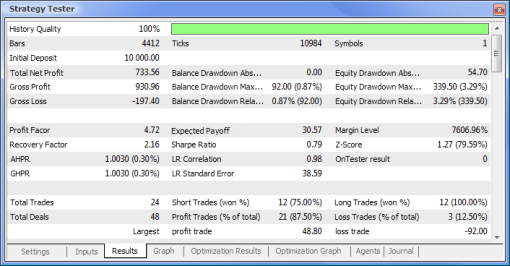
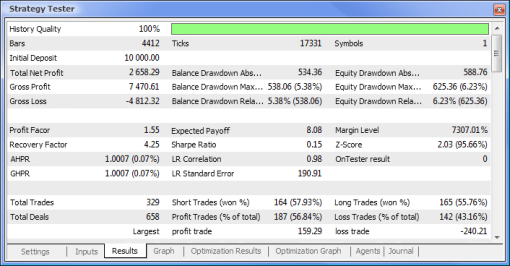
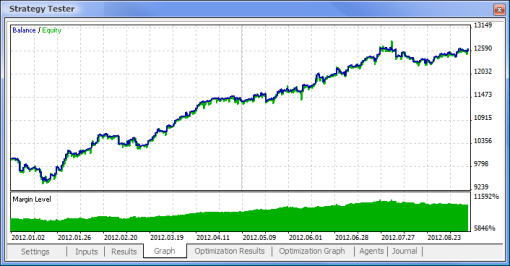
图 10. 测试报告
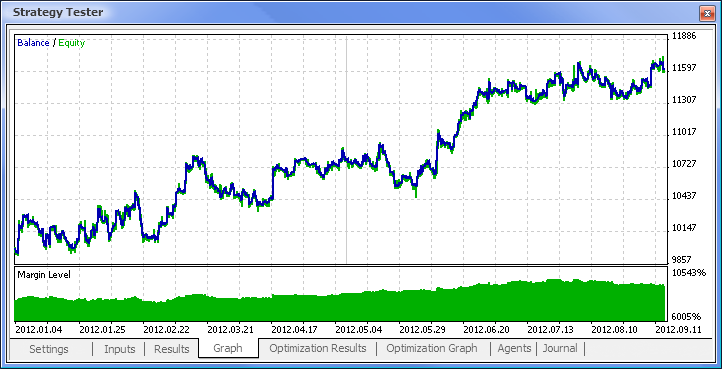
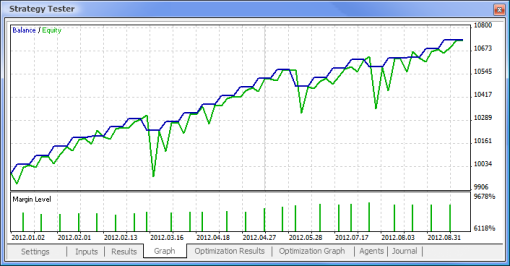
图 11. 余额图
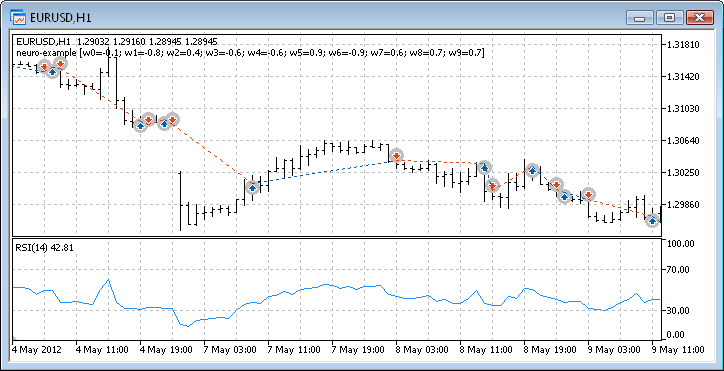
图 12. EA 的交易性能
这样,我们最终获得了结果,并且对于刚开始而言,它们并不算差。请记住,我们仅有一个神经元。提供的例子相当原始,但是我们必须承认即使单独使用它也能盈利。
神经网络的优点
现在,让我们尝试将一个依据标准逻辑的 EA 与一个神经网络驱动的 EA 进行比较。我们将比较随客户端提供的 MACD 示例 EA 和基于 MACD 的神经网络驱动 EA 的优化与测试结果。
在优化中不涉及 Take Profit(获利)和 Trailing Stop(跟踪止损)值,因为在神经网络驱动 EA 中不存在这两项。我们要测试的两个 EA 都以具有以下参数的 MACD 为基础:
- 快速移动平均线周期: 12;
- 慢速移动平均线周期: 26;
- 差异平均周期: 9;
- 价格类型:收盘价。
您还可以设置需要的货币对和时间框架,但是在我们的例子中,我们将保持它们不变 – 分别为 EURUSD、H1。两个例子中的测试周期是相同的:从一年的开头开始,使用开盘价。
| MACD 示例 | MACD 神经网络示例 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
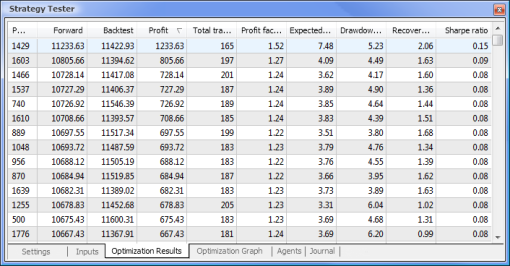 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
现在,让我们比较所测试 EA 的关键参数:
| 参数 | MACD 示例 | MACD 神经网络示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 总净利润 | 733,56 | 2 658,29 |
| 余额亏损绝对值 | 0,00 | 534,36 |
| 市值亏损最大值 | 339,50 (3,29%) | 625,36 (6,23%) |
| 盈利系数 | 4,72 | 1,55 |
| 回收系数 | 2,16 | 4,25 |
| 预计获利 | 30,57 | 8,08 |
| 夏普比率 | 0,79 | 0,15 |
| 总交易次数 | 24 | 329 |
| 总成交次数 | 48 | 658 |
| 盈利交易次数(总交易次数的%) | 21 (87,50%) | 187 (56,84%) |
| 平均获利交易 | 44,33 | 39,95 |
| 平均连续盈利次数 | 5 | 2 |
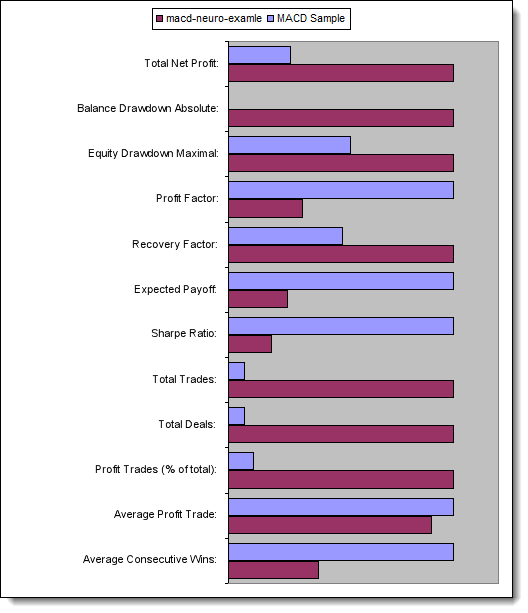
图 13. 关键参数的比较
总结
本文介绍了使用神经网络设计 EA 时需要知道的要点。它向我们说明了神经元和神经网络架构的结构,概要介绍了激活函数以及改变激活函数形状的方法,还说明了优化和输入数据正态化的过程。此外,我们将一个依据标准逻辑的 EA 与一个神经网络驱动的 EA 进行了比较。
本文译自 MetaQuotes Software Corp. 撰写的俄文原文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/497
MyFxtop迈投(www.myfxtop.com)-靠谱的外汇跟单社区,免费跟随高手做交易!
免责声明:本文系转载自网络,如有侵犯,请联系我们立即删除,另:本文仅代表作者个人观点,与迈投财经无关。其原创性以及文中陈述文字和内容未经本站证实,对本文以及其中全部或者部分内容、文字的真实性、完整性、及时性本站不作任何保证或承诺,请读者仅作参考,并请自行核实相关内容。
著作权归作者所有。
商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。

 MyFxTops邁投財經
MyFxTops邁投財經
